Contents
IPv6 installation for Windows users
What is the status of IPv6 support in Microsoft Operating Systems?
IPv6 is officially supported in Windows XP after Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2003 (any version) and in Windows Vista.
There is experimental support for IPv6 in Windows XP (without service pack).
There is a Microsoft Research implementation for Windows NT4.0 and Windows 2000 here: http://research.microsoft.com/msripv6/msripv6.htm
There is a Technology Preview implementation for Windows 2000 here: http://msdn.microsoft.com/downloads/sdks/platform/tpipv6.asp
Unless there is a reason for it, the Windows XP SP1 (or later) and/or Windows Server 2003 implementation should be used for IPv6.
There is no Microsoft implementation of IPv6 in the 95/98/ME line of Microsoft Windows, however there is an IPv6 protocol stack for Windows 95/98 and Windows NT at http://www.trumpet.com.au/winsock/winsoc5.html
How to enable IPv6 in Windows XP (service pack 1 and later) or in Windows Server 2003?
IPv6 is officially supported in XP from Service Pack 1 and later and in Windows Server 2003. Because there are other serious reasons to install service pack 1, the following applies to XP SP1, with the differences noted later.
IPv6 can be installed the same way, as any other network protocol. Go to Control Panel, networks, network connections. Right click on the network connection, choose properties! Then Add, Protocol, Microsoft TCP/IP version 6.

That's all! IPv6 should be up and running. Use the command line utility ipconfig to verify the IPv6 addresses and interfaces.
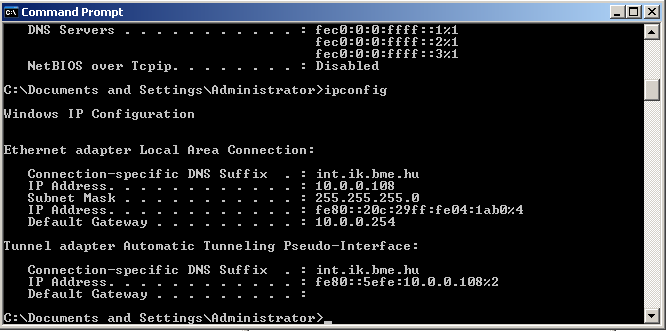
How to enable IPv6 in Windows XP (no service pack)?
On Windows XP, no service pack, IPv6 is not available in the Add protocols dialog, it can be installed by typing ipv6 install on the command line. The ipv6 command can be used to verify operation.
If IPv6 is installed on a machine without service pack, and later upgraded to SP1, ipv6 uninstall is necessary to have IPv6 installable from control panel.
What is new for IPv6 in Windows XP SP2?
Windows XP SP2 includes the updates to IPv6 that are also included in the Advanced Networking Pack for Windows XP plus some bug fixes for IPv6:
; IPv6 ICF : IPv6 Connection Firewall that allows filtering unsolicited incoming IPv6 traffic. ; Teredo : Teredo, also known as IPv6 NAT traversal, is an IPv6/IPv4 transition technology that provides unicast IPv6 connectivity across the IPv4 Internet when the communicating peers are separated by one or more NATs. This is kind of hack that can be avoided most of the cases with proper setup of NAT boxes (i.e.: providing NAT and IPv6 connectivity in the same time). ; Host specific relay : The portproxy is a tool that act as proxies between IPv4 and IPv6 networks and applications
How to enable IPv6 in Windows Vista?
IPv6 is enabled by default in Windows Vista. It can be disabled by uninstalling the IPv6, or different IPv6 features may be enabled or disabled individually by setting the following registry value:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\tcpip6\Parameters\DisabledComponents
The value can be the combination (logical or) of the follwoing values:
1 |
Disable tunnel interfaces |
2 |
Disable 6to4 |
4 |
Disable ISATAP |
8 |
Disable Teredo |
16 |
Disable LAN and PPP interfaces |
32 |
Set preference of IPv4 over IPv6 |
255 |
Disable IPv6 completely |
How can I configure IPv6 on Windows systems
You should use netsh commands in interface ipv6 context to query and configure IPv6 interfaces, address, caches, and routes. As a backward compatibility interface you can use ipv6.exe command (' Note: ipv6.exe command is not available on Windows 2003 machines.').
How can change the address selection policy?
In Windows XP and Windows 2003 you can define address selection defined RFC 3484. For this purpose you can use netsh interface ipv6 command.
- Adding policy rule
netsh interface ipv6 set prefixpolicy <prefix> <precedence> <label>
- Showing policy rules:
netsh interface ipv6 show prefixpolicy
- Clearing policy rule table
netsh interface ipv6 clear prefixpolicy
See some examples in FreeBSD configuration section.
What is different in Windows Vista?
Windows Vista supports IPv6 out of the box and it is enabled at installation. There is now graphical user interface for setting basic IPv6 parameters, available through the properties button on the properties panel for the network connection.
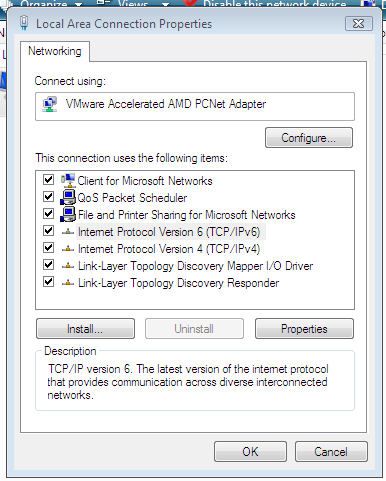
Setting IPv6 properties
Using the IPv6 properties pane, manual or automatic address configuration can be selected. Vista will use stateless autoconfiguration to obtain prefix and gateway information or DHCPv6 to obtain DNS server information. On the Advanced Settings pane, multiple addressess and gateway can be selected.
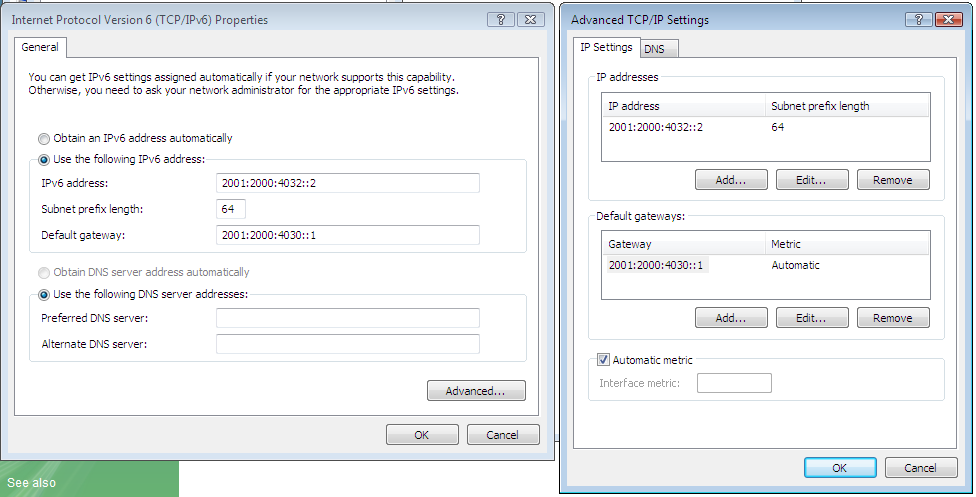
IPv6 parameters can also be set using the
netsh interface ipv6
command. For example to set IPv6 address, the
netsh interface ipv6 add address 5 2001:2000:4030::2
can be used. 4 is the interface index, which can be queried with
netsh interface ipv6 show interface
command. Instead of the interface index, the interface name (such as "Local Area Connection") may be given.
Vista applications
Internet Explorer 7 and Windows Mail (Outlook Express in Vista) supports IPv6, without further configuration. In IE7 it is possible to enter literal IPv6 addresses in the address bar. Windows Mail uses IPv6 if the domain name for the servers resolvs to IPv6.